Match the Type of Mutation to Its Definition.
Up to 24 cash back Types of Mutations For Questions 18 match the term with its definition. Definition of mutation.

Evolution Vocabulary Distance Learning Vocabulary Lessons Life Science Lessons Life Science
In biology mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes which typically manifest physically.
. A heritable change in genetic information. A change in one or a few nucleotides that occur at a single point in the dna sequence f 3. The change ofone base to another in a DNA sequence 2.
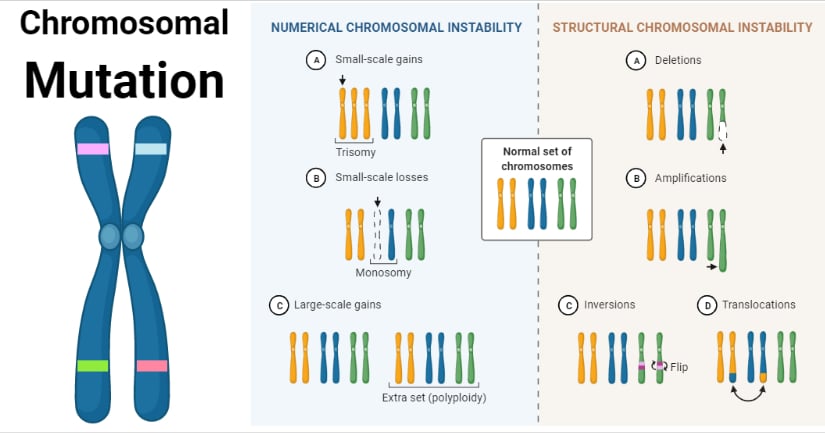
Do not change the amino acid sequence of the gene product the protein Mutations that replace a codon with a different codon resulting in. Bio quiz mutations 22 terms. ___________________ mutations are changes that alter the structure of the chromosome itself.
The resulting protein is usually nonfunctional. DNA and RNA are made up of many nucleotides. Match the type of chromosomal mutation with its definition.
Thymine is removed Adenine is replaced with thymine and guanine 1. The simplest and the most harmless are. A change in one or a few nucleotides that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence F 3.
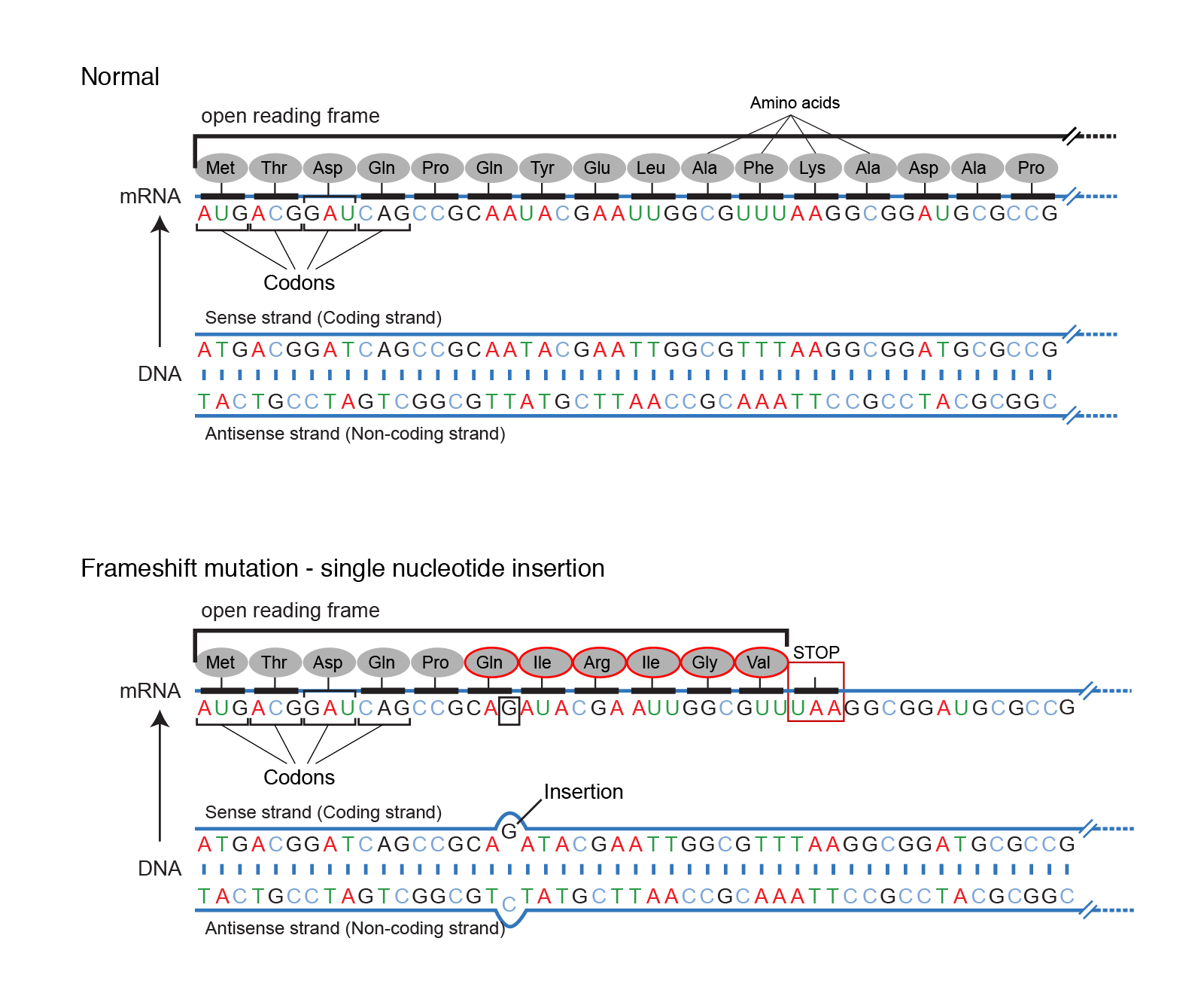
This results in an altered protein product that has a different amino acid sequence than the original. Cytosine guanine adenine thymine in DNA and uracil in. A reading frame consists of groups of 3 bases that each code for one amino acid.
Part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another 4. Click card to see definition. Based on change in genotype and phenotype mutation are of two types.
When due to a point mutation there is change in the sequence of base pair leading to stop codon. The change of one base to another in a dna sequence c 2. Single nucleotide substitution Adenine thymine and guanine are.
Small-scale mutations are types of gene mutations such as those affecting a small gene in one or a few nucleotides including. MUTATION The replication and distribution of genetic material is extremely accurate so that the genetic information is usually passed on from one generation to the next without alteration. There are five different molecules that can make up nitrogenous bases on nucleotides.
Frame-shift mutation Guanine is replaced with cytosine 2. The effect of a mutation can depend on the region in which the sequence of genetic material has been changed. Answers 13 3 mutations types of mutations for questions 1 8 match the term with its definition.
Tap again to see term. ___mutations are changes that alter the structure of the chromosome itself - chromosomal. Add or delete 1 or 2 nucleotide letters thereby changing the reading frame for the gene.
Here is a quick summary of a few of these. Delahunty biology honorsmutations worksheet name key. Part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another 4.
The change of one base to another in a DNA sequence C 2. - Polygenic traits - Quantitative traits - Monozygotic twins - Dizygotic twins - Short tandem repeats - Transcription - Ribonucleic acid - Mutation - Stem cell - Reproductive cloning A. Click again to see term.
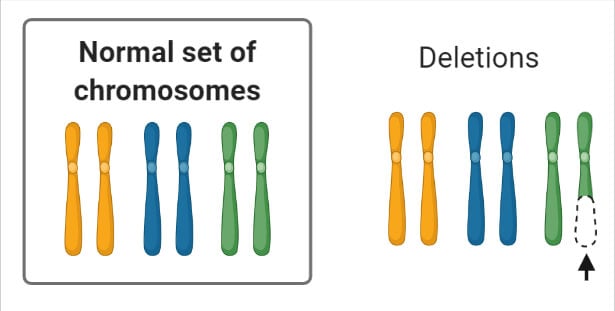
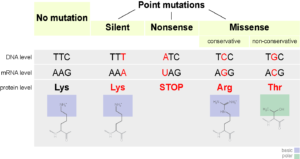
Please match each type of mutation with its appropriate description. Match the type of chromosomal mutation with its definition - deletion- loss of a portion of a chromosome. A mutation that results in changing a codon such that a different amino acid is specified.
Two types - Transitions Purine to other purine or pyrimidine to other pyrimidine. A change in the nucleotide. Macro social work 2 89 terms.
- Insertions of new DNA again ranging from 1 to many base pairs - Point mutations. A heritable change in genetic information 5. Answers 133 Mutations Types of Mutations For Questions 18 match the term with its definition.
It occurs as a result of replacement of one nucleotide by other in specific nucleotide sequence of gene. Match each word or phrase with its definition. Definition Term B H G 1.
Tap card to see definition. A point mutation is a type of mutation in DNA or RNA the cells genetic material in which one single nucleotide base is added deleted or changed. At the simplest level a mutation is a change or transformation.
A mutation is said to be punctual when it touches one or more nucleotides of the same gene. Point mutation brings little phenotypic change as compared to frameshift mutation. It refers to any change in the sequence of DNA which has no further impact on the amino acid sequence in a protein or in the functions performed by a protein.
Point Mutation Definition. Place the types of mutations found in humans in the correct order going from most frequent to least frequent. Match the type of mutation with its definition.
Gene mutations and chromosomal mutations are two broad categories in which the mutation is classified. A change in one or a few nucleotides that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence 3. This type of mutation happens when a single base in DNA is substituted with another base for example an A becomes a G.
Match the types of mutations to their definition. Types of mutations - Deletions a part of the DNA is missing anywhere from 1 base pair to parts of chromosomes. Duplication a loss of a portion of a chromosome b copying a portion of a chromosome c a piece of a chromosome is broken off and joined to another chromosome d segment of chromosome is broken in 2 places reversed and put back together.
The change of one base to another in a DNA sequence 2. By the replication errors exposure to mutagens and viral infections change or alteration occurs in a DNA sequence that causes genetic abnormalities known as mutation. A change in one or a few nucleotides that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence 3.
A mutation that changes a codon that specifies an amino acid to a stop codon resulting in premature termination of polypeptide synthesis. There is no phenotypic indicator of mutation. Point mutation are two types based.
Note that not all definitions will be used. This type of mutation occurs when the addition or loss of DNA bases changes a genes reading frame. A frameshift mutation shifts the grouping of these bases and changes the code for amino acids.
There are many different ways that DNA can be changed resulting in different types of mutation. Up to 24 cash back 133 Mutations Types of Mutations For Questions 18 match the term with its definitio n. Part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another A 4.
Substitution A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another ie a change in a single chemical letter such as. But occasionally errors do occur both during replication and distribution of the genetic material giving rise to sudden heritable changes in the characters of organisms. An undifferentiated cell that has not yet been programmed and can become any type of cell B.

Point Mutation Definition Types Expii
Chromosomal Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples
Chromosomal Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples
Types Of Mutations Mt Hood Community College Biology 102

Mutation Definition Causes Types Facts Britannica

Plant And Animal Cells Vocabulary Sort Science Vocabulary Science Vocabulary Activities Animal Cell

133 Genetic Mutations Biology Notes For A Level Biology Notes Genetics Science Biology
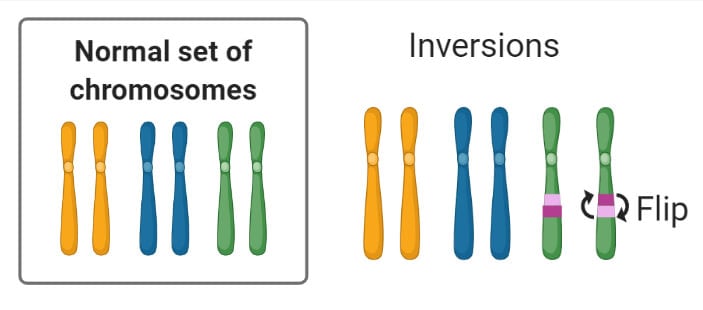
Chromosomal Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples

Insertion Dna Mutation Definition Examples Expii
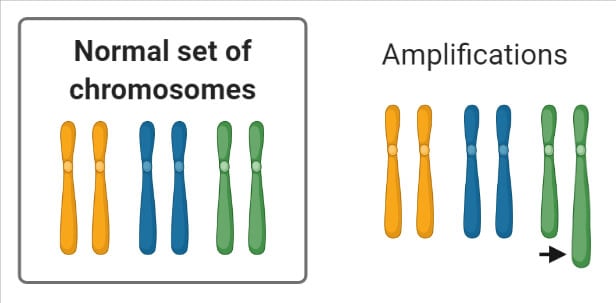
Chromosomal Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples

Deletion Mutation Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary

Dna Mutations Practice Worksheet With Answer Key Laney Lee Scientific Method Worksheet Practices Worksheets Worksheets

Difference Between Gene Mutation And Chromosome Mutation In Tabular Form Chromosome Mutation Biology

Point Mutation Versus Frameshift Mutation Point Mutation Mutation Brain Facts

Substitution Mutation Definition Examples Types Biology Dictionary

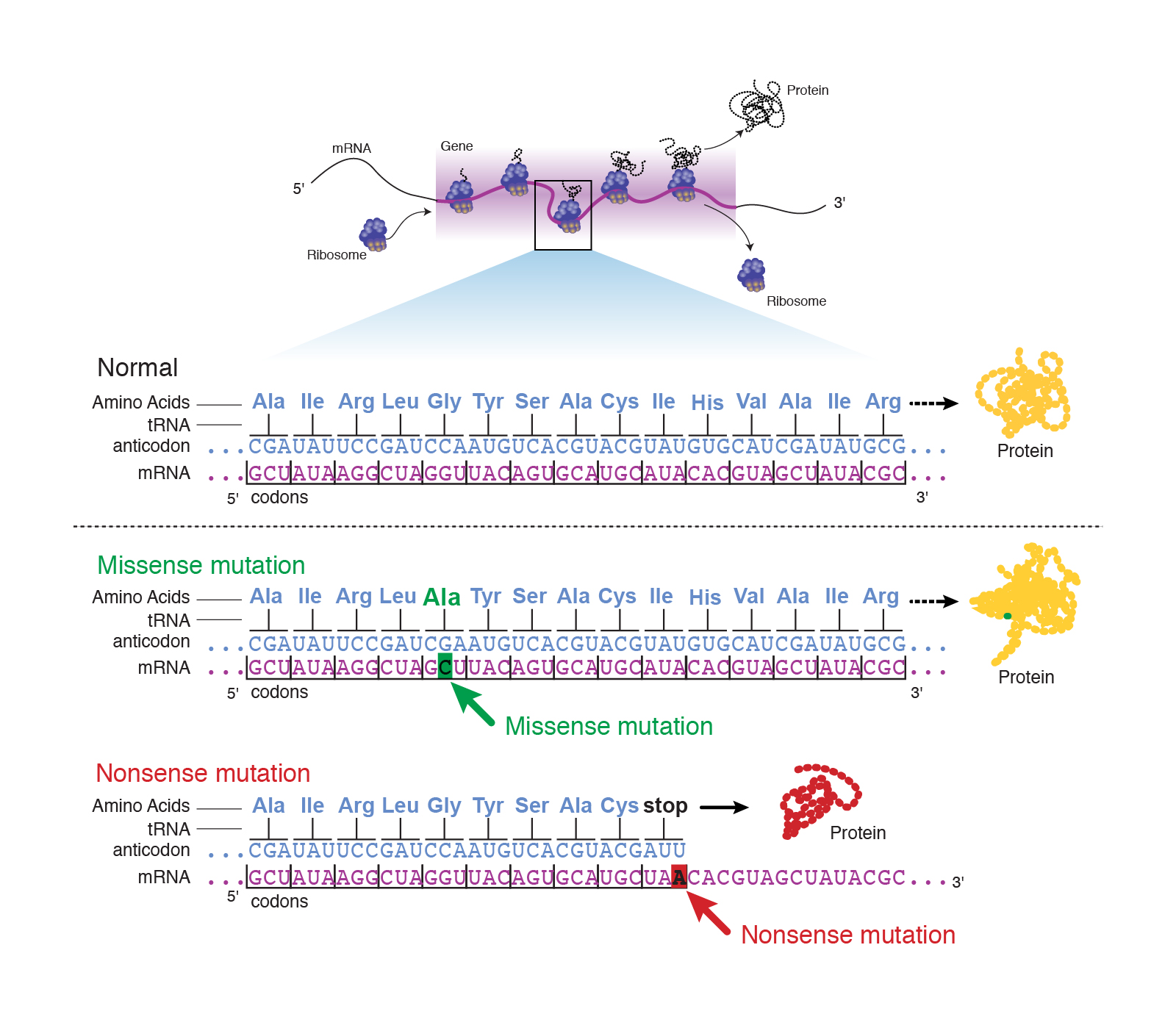

Comments
Post a Comment